On June 13, 2023, Aliaksandr Lukashenka announced that he had already received the first nuclear warheads from Russia, and those are “bombs three times more powerful than Hiroshima and Nagasaki. One bomb is three times more powerful. It means, well, I don’t know, up to a million people will die at once”.
Is Aliaksandr Lukashenka able to seize control of the nuclear weapons deployed in Belarus?
We have grounds to believe that Aliaksandr Lukashenka has an opportunity to override and take charge of the nuclear weapons belonging to the Russian Federation, but deployed in the territory of Belarus.
This our investigation has an “invisible” part, consisting of personal conversations of the investigators with various persons in different years, holding high-ranking positions in the army and in other enforcement structures, with engineers and employees of Belarusian defense enterprises, with politicians (including the late Stanislav Shushkevich) and specialists on weapons. Step by step, they gelled an understanding of how exactly Aliaksandr Lukashenka can seize control over the Russian nuclear weapons deployed in Belarus.
In short, the point is that all the control systems of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation are similar to or are successors of the systems developed and implemented in the USSR. Especially, it concerns the nuclear weapons in the first place. One of the main centers for development and production of electronics, computing hardware, as well as of control systems in the Soviet Union was Belarus (Belarusian Soviet Socialist Republic at the time). Moreover, a lot of enterprises involved in that industry then, kept their specialization, specialists, and today continue to be involved in the same activity.
We cannot say unequivocally, the Aliaksandr Lukashenka is planning to gain access to the control systems of the Russian nuclear weapons, when it arrives to Belarus. However, there are plenty of indirect indicators that such version of events is probable. Also, there is a totally obvious desire of the Belarusian dictator to lay hands on nuclear weapons, and he does not hide it. We repeat: that scenario is a non-zero probability, therefore it deserves special attention of the international community. Otherwise, the humanity is at risk to have another crazy dictator with nuclear weapons in the centre of Europe.
Aliaksandr Lukashenka and nuclear weapons: history of the relationship
It is known that at the signing of the Belovezhskaya agreements (about liquidation of the USSR), the nuclear issue was discussed: according to the Minister of Foreign Affairs of Belarus, Piotr Kravchenko, the documents stipulated that the nuclear weapons command center shall be controlled by all the CIS states, and Russia was not recognized as a legal successor of the “nuclear suitcase”. Due to that, Russia was at risk to lose its nuclear status. Commenting on that issue, Kravchenko said that “renunciation happened later”.
Here’s a fragment of one of the conversations of the author of this investigation with Stanislav Shushkevich, the leader of Belarus in 1991-1994, and the person who signed the Belovezhskaya agreements from the side of Belarus and the agreement on the renunciation of nuclear weapons by Belarus.
Author: Why did Belarus, as well as Ukraine, decided to renounce its nuclear arsenal?
Stanislav Shushkevich: Can you imagine, how much it costs to store and guard nuclear weapons, maintain its efficiency, modernize it? Belarus just would not have any budget for it in the 90s… Let’s add here very strong pressure from the West who was fearing that the USSR nuclear weapons would spread.
A.: As I understand, there was no sense to keep weapons that you cannot actually use anyway?
S.Sh.: Actually, we were able to use it. All the technology was created by us, by our specialists in electronics. The issue was not that. However, who against would we use it? And why? At that moment all that seemed completely unreasonable.
A.: Have you ever regretted you had given up nuclear weapons?
S.Sh.: Never! Since now I understand it could have got in to the hands of Lukashenka. And he is a complete psychopath, without any moral barriers. He would start blackmailing everybody with nuclear weapons.
Now Moscow says that Belarus has been asking it to deploy Russian nuclear weapons in its territory for a long time. Indeed, Aliaksandr Lukashenka publicly announced that as far back as in the year 2021, supposing that NATO would deploy nuclear bombs in Poland.
In general, Aliaksandr Lukashenka has said many times that he considers the decision to withdraw nuclear weapons from Belarus made in 1992 a mistake. In February, 2022, for another time Lukashenka announced that nuclear weapons might be deployed in Belarus in case of threats coming from the West. He added that he would ask the Russian Federation to create a military center in Belarus for assimilation of Iskanders, as Belarus was planning to buy that type of arms.
In June, 2022, during a meeting with Putin in Saint Petersburg, Lukashenka proposed to take tit-for-tat measures in the military sphere to the “actions of the West” and “adjust” Belarusian airplanes to carry nuclear warheads. In the August of the same year, Lukashenka stated that reequipment of Belarusian airplanes into nuclear weapon carriers had already been completed.
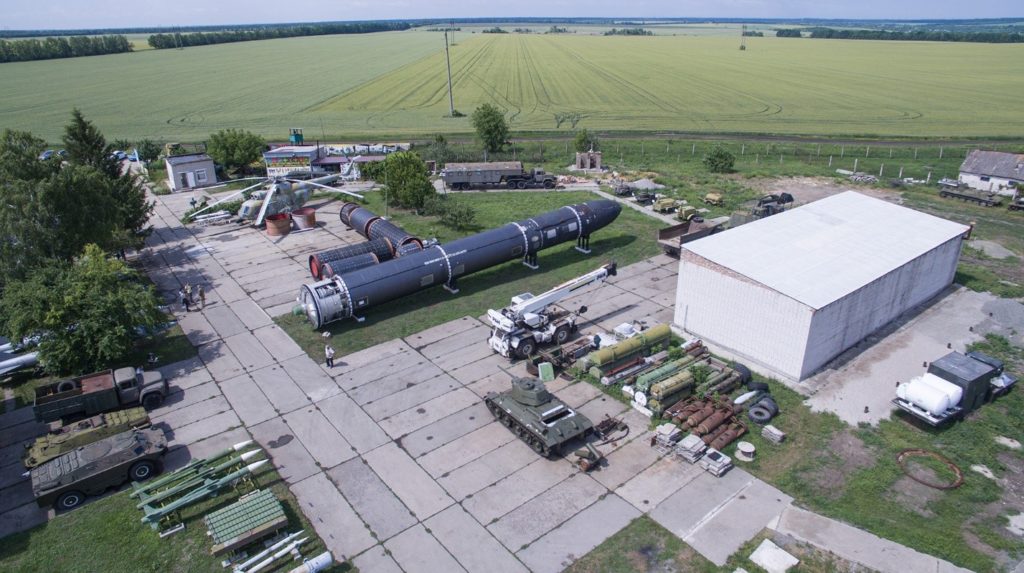
On March 22, 2023, in Khatyn, commenting on the plans of Great Britain to deliver depleted uranium munitions to Ukraine, Lukashenka said that “Russia will deliver us munitions with real uranium”. At the time, that phrase was perceived as something stupid of Lukashenka to say, his typical “tongue incontinence”. Hoever, on March 25, 2023, it was really announced that Moscow and Minsk had reached an agreement to deploy tactical nuclear weapons in the territory of Belarus. According to Vladimir Putin, as well as to Russian and Belarus military, 10 Belarusian airplanes had already been adjusted to carry nuclear warheads; also, Iskander operational-tactical missile systems capable of using nuclear-armed missiles had been transferred to Belarus. On April 3, 2023, training of the Belarusian crews and construction of nuclear weapons storage facilities started.
Belarusian and Russian propagandists spoke about that decision exclusively in the glowing terms: for example, they called deployment of weapons of mass destruction in our country a “historical chance” and “soft military power”.
In order to use tactical nuclear weapons, Su-25 attack aircrafts were improved and MiG-29 fighters were modernized in Belarus. Besides that, a small number of Su-24M front-line bombers are undergoing major overhaul, the ones that were the main carriers of air tactical nuclear in the late Soviet Union. Also, Iskander systems have already been delivered and deployed in Belarus, whose missiles can be armed with nuclear warheads. The strike range of Iskander system missiles constitutes up to 500 kilometers.

Iskanders can shoot both ballistic and cruise missiles. A nuclear warhead definitely exists for the first type of them, its model was demonstrated at the weapons exhibition “Army-2018”. According to the estimates, such a warhead can have the capacity from 5 to 50 kilotonnes of TNT equivalent. If the first value is relatively low (about a quarter of the capacity of the American bomb Little Boy, thrown on Hiroshima in 1945), the bomb of 50 kilotonnes is capable to destroy a whole city.
Nothing is really known about the nuclear warhead for the R-500 cruise missile, used in the Russian complex. However, there is information that the missile is able to deliver a warhead weighing 480 kg, approximately the same, as ballistic missiles of Iskander and Kalibr missiles, that can carry nuclear warheads.
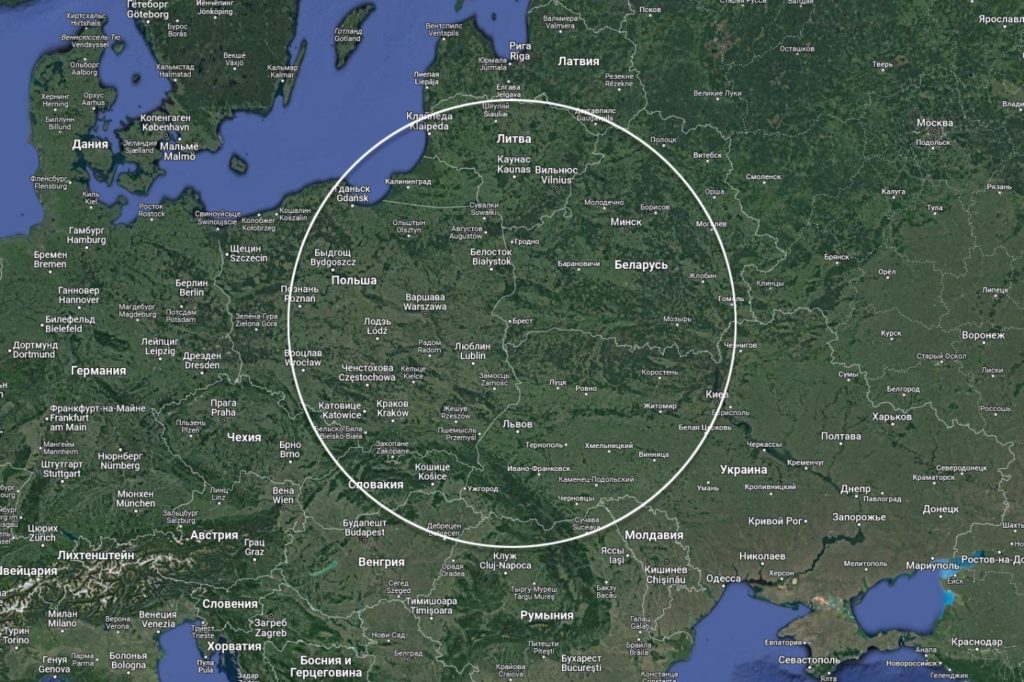
Reasoning from the standard strike range of Iskander equal to 500 kilometers, the countries of the Eastern Europe turn out to be within striking distance of missiles deployed in the west of Belarus: Ukraine, Poland, Baltic countries, Slovakia, a part of Czechia, Hungary, Romania and Moldova. Nevertheless, not everybody believes that Iskanders can shoot only at the distance of 500 kilometers. Thus, New York Times wrote that a cruise missile for a Russian complex is a variant of a ground-launched Kalibr missile. Considering that the striking range of a Kalibr missile is estimated at 2500 kilometers, almost the whole Europe, except Portugal, can be hit by such missiles. However, that information has not been confirmed.
On April 3, 2023, the Press Secretary of the President of Russia, Dmitry Peskov, when asked to precise who is going to control tactical nuclear weapons in Belarus, called on to use statements of Vladimir Putin as a reference.
In his intervie on March, 25, Vladimir Putin said that Moscow and Minsk came to an agreement to deploy tactical nuclear weapons in the territory of Belarus, as Aliaksandr Lukashenka has allegedly “been asking for a long time” about that. According to the Russian president, construction of a special storage facility for that kind of weapons will have been finished by July 1, 2023.
Putin added that Russia does not transfer tactical nuclear weapons to Belarus, but is only deploying it there, and that does not violate the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons. “We are not transferring them. And the USA are not transferring them to their allies. In general, we are doing the same things they have been doing for decades. They have allies in certain countries, and they equip their carriers and train their crews. We are going to do the same thing”, he said.
However, on March 31, 2023, during his annual address to the parliament and the people, when answering the question how the control of the tactical nuclear arsenal planned to be deployed in Belarus was going to be organized and whether the opinion of the country would be taken into consideration on the day X, Lukashenka said the following: “Everything is going to happen according to the law and to the rules. There is no uncontrolled weapons in Belarus and there cannot be. Therefore, we are going to control here in Belarus everything that we have.”
Therefore, it turns out that Aliaksandr Lukashenka has openly admitted his plans to have access to the control systems of the Russian nuclear weapons deployed Belarus. It is quite difficult to understand his words in any other way.
Already on April 4, 2023, the press service of the Ministry of Defence of the Republic of Belarus informedthat squadrons of Iskander-M operational-tactical missile systems of the missile forces of the armed forces of the Republic of Belarus went to the Russian Federation for practical training. The Belarusian military were sent to one of the Russian training grounds where they fulfilled a complete course of training, improved their practical skills of preparation of a missile system for operation and trained in its deployment. They also conducted combat training launches. “Besides that, the military personnel will have to learn in detail the issues of maintenance and use of tactical nuclear ammunition of the Iskander-M operational-tactical guided missile systems“, said the communication of the Ministry of Defense.

On April 14, 2023, the Defense Minister, Viktor Khrenin, stated that if needed, also strategic nuclear weapons will appear in Belarus. “We have our military hardware prepared, which includes aircrafts able to carry nuclear ammunition. We have trained pilots. We have received the most modern Iskander system able to use missiles with nuclear warheads”, reminded Viktor Khrenin.
“If necessary, we will get strategic nuclear weapons as well”, claimed the head of the Belarusian military establishment. Viktor Khrenin assured that Belarus has already started preparation of the strategic weapons sites of the country.
Types and quantity of the nuclear weapons
All the nuclear weapons of the Russian Federation is divided into tactical and strategic. Premised on parallel obligations of the USA and the USSR / Russia of the beginning of the 90s of the last century on the reduction and elimination of tactical nuclear weapons (TNW), TNW include shorter-range missiles, artillery assets and nuclear mines (ground bombs) of land forces, surface-to-air missiles of anti-aircraft weapon systems, missiles and bombs (including depth bombs) of striking non-strategic aviation of the Air Force/Navy, as well as various tactical anti-aircraft missiles, anti-ship and anti-submarine missiles, depth bombs and torpedoes of combat ships and multi-mission submarines.

TNW use dual-purpose delivery vehicles (medium bombers, fighter-bombers, short-range offensive missiles and anti-aircraft missiles, combat equipment of ships and submarines, large-calibre cannon artillery. Such delivery vehicles are place on launch multi-mission, dual-purpose ships and submarines. That is why, unlike strategic nuclear forces (SNF), reduction or elimination of the TNW is impossible to be conducted or controlled through elimination of launchers, delivery vehicles or platforms, as almost all of them make part of armaments for general purpose forces and are designed mostly for use in regular combat operations.

Unlike SNF, Russian non-strategic nuclear means are hidden behind a thick curtain of secrecy even more. According to the estimates of Carnegie Endowment for International Peace (based in Washington, D.C.), for Russia there remains a huge advanatge over the USA and the NATO on that class of nuclear weapons. According to some data, at the end of the 80s, the Soviet stockpile of tactical nuclear weapons consisted of up to 22,000 units. According to unilateral presidential initiatives of the USSR and Russia of the years 1991-1992, adopted in response to the moves made by the USA and in connection with the collapse of the Warsaw Treaty Organization and the USSR, a number of radical measures were planned. It was intended to relocate all TNW of the Land Forces to facilities bases of nuclear weapons assembly plants and to centralized storage facilities in order to destroy them, eliminate 30% of the Navy TNW, as well as 50% of warheads of surface-to-air missiles of anti-aircraft weapon systems and 50% of the Air Force means.
According to the available data, by the year 2000, all the TNW of the Feet and Aviation of the Russian Navy had been moved to centralized storage facilities, and 30% of those means were liquidated. There were eliminated 50% of the TNW of the Air Force and 50% of warheads of surface-to-air missiles of anti-aircraft weapon systems. Also, nuclear artillery and tactile missile warheads and mines of the Land Forces were partially destroyed.
At the present moment, most expert estimates come down to about 2000 medium range and tactical nuclear weapons units in Russia’s possession. The number includes about 500 tactical nuclear aviation missiles and bombs for 120 medium-range Tu-22M-type bombers and for 400 Su-24 type front-line bombers. Besides that, there are about 300 aviation missiles, free-fall bombs adn depth bombs for the naval aviation consisting of 180 Tu-22M, Su-24, Be-12 and IL-38 aircrafts. Over 500 units of tactical nuclear weapons consist of antiship, antisubmarine, and antiaircraft missiles, as well as depth charges and ship and submarine torpedoes, including up to 400 long-range multi-purpose submarine-launched cruise missiles. About 100 nuclear warheads are assigned to A-135 Moscow missile-defense system interceptor missiles and 630 more – to S-300 anti-aircraft missiles and other air-defense system of the territory. It is considered that in peace time all those nuclear means are stored at specialized storage facilities of the Russian bases of the Air Force, the Navy and the Air Defense.
As it has been mentioned before, in the course of the 90s, all the means of the tactical nuclear weapons of the Land Forces and the Air Defence, as well as the major part of the tactical nuclear weapons of the Air Force and the Navy were redeployed to at centralized storage sites of the 12th Main Directorate of the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation (the nuclear and engineering maintenance forces), where they are kept as a reserve or queue for dismantling and disposal. It is not totally clear, whether it concerns the storage facilities of the Repair and technical base of the Navy and the Air Force, transferred under the control of the nuclear and engineering maintenance forces of the 12th Main Directorate of the Ministry of Defense, or that refers only to the previously built specialized centralized storage facilities of that Directorate. The latter also store warheads and other weapons of strategic nuclear forces. Their total quantity is kept secret, but foreign specialists agree on the figure of about 8000 units. Also, the methodology of calculation of independent experts arises question, in particular, the 630 warheads of the air defence missiles included into the total quantity of the TNW, which according to Moscow have been placed to centralized storage facilities.

At the same time, operational-tactical systems are being updated by means of deployment of Iskander-type tactical missiles, that can be equipped with both conventional and nuclear warheads. New front-line bomber Su-34 also has a dual purpose, which means they can carry also tactical nuclear munitions.
As we see, today the Russian Federation has more than enough units of TNW to deploy in Belarus among other places in the framework of their West-intimidation policy. Yes, formally, neither Russia, nor the USA possess a right to transfer their nuclear weapons to other countries: it is forbidden by Articles 1 and 2 of the Non-Proliferation Treaty. In Belarus, tactical weapons will be at the disposal of the nuclear and engineering maintenance forces of the 12th Main Directorate of the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation. It is a separate kind of troops which can transfer tactical nuclear weapons to troops only by the order of the supreme commander of the armed forces of the Russian Federation, which is the president. Also, that directorate is accountable only to him directly.
However, in the situation of chaos in Russia which will arise in the result of the defeat in the war against Ukraine or “just” in case of Vladimir Putin’s death, it is unlikely that the 12th Main Directorate of the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation will be able to act in the territory of Belarus in order to, for example, move the nuclear warheads back to Russian territory. Belarus has enough military force to defend the TNW which are already in its territory from such attempts. Also, such “nationalization” of the TNW will inevitably be followed by a switch of their control channels from Moscow to Minsk. Being in a situation of chaos, Russia will not be able to object to it.
How the Russian Nuclear Arms Management System works
The management of the strategic nuclear forces of the Russian Federation (SNF RF) is totally centralized, and the symbol of that management is the so-called “nuclear suitcase” of the president of Russian Federation. It is a portable subscriber complex (cipher) “Cheget” of the automated control system of strategic nuclear forces “Kazbek” (also known as “Kavkaz-7”). The development of the system started in the 1970s at the Leningrad Special Design Bureau OKB “Impulse” by the initiative of T. N. Sokolov, the chief designer of the Soviet system of combat control of the Russian Strategic Nuclear Forces.
Actually, Cheget is a sort of a telephone set with a conference call option, from which the information is transferred not by voice, but with the help of special symbols-cyphers. Also, Cheget is a special programming unit that allows to access the command post of the Directorate of the General Staff of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation and the reserve posts through a sputnik.
In the first 30 years of exploitation of “nuclear suitcases” quite a huge number of such devices were produced: it was justified by the necessity to change the encryption keys every 5 years. There is always equipment for provision of reconnaissance-protected classified communications near every such suitcase. It is also known that one of the components of a suitcase is an individual memory card.
The initial resource of the Kazbek system was 10 years, and it had to be urgently upgraded and modernized in the following years to ensure the necessary level of nuclear security. However, the means for the exploitation of that system were catastrophically scarce. The situation was aggravated when almost all the microelectronic industry of the former Soviet Union turned out to be abroad after its collapse, first of all, in Belarus (pay attention to that!). Moreover, civil scientists from various scientific research institutes participated in the designing of Kazbek, and following the collapse of the USSR, due to chronic underfunding and salary debts, the number of employees of those organizations, capable to solve the issues of maintenance of the “nuclear suitcase” decreased drastically. Due to that, in the February of 1997, the Defense Minister, Igor Rodionov, warned Boris Yeltsin that the situation of nuclear security in the country was critical, and a month later in the Ogoniok magazine concerns were raised that they were going to carry not the real “nuclear suitcase” behind the president, but a dummy, as it was not possible to repair it. In 1998, all the technicians resigned from one of the classified enterprises because of the non-payment of salaries, which jeopardized the existence of a system of warning and response to a nuclear attack.
However, later the problem was solved: Russia began to grow rich rapidly due to active sale of oil and gas in the world market, enough financial means arrived to the budget, and now they were able to modernize the Strategic Nuclear Forces control system by efforts of Russian defence industry enterprises.
Everything said above is evidence that Russian strategic nuclear weapons are subject to a completely centralized and quite safe control system, any interception of its control is hardly probable.
Nevertheless, the situation with the tactical nuclear weapons is totally different. It should be understood, that in war time, the tactical nuclear weapons are deployed as part of the general forces and can be immediately involved into the conflict with a high risk of rapid nuclear escalation. As the experts of the American expert-analytical center “Carnegie” rightly believe, the TNW is not equipped with the same secure systems of unauthorized use prevention, as the SNF, due to what the danger of inadvertent nuclear strike becomes significantly greater. In other words, the probability of malicious takeover of control of such weapons is much higher. Also, the “Carnegie Center” notes that TNW means (especially of old types) situated at forward operating bases (and in Belarus, they are going to be placed exactly at the forward operating bases) are less secure from theft, they have smaller weight and size characteristics, as well as less effective code-locking devices, and therefore they present a tempting object for terrorists as well as for all those who may want to come into possession of that type of weapons illegally.
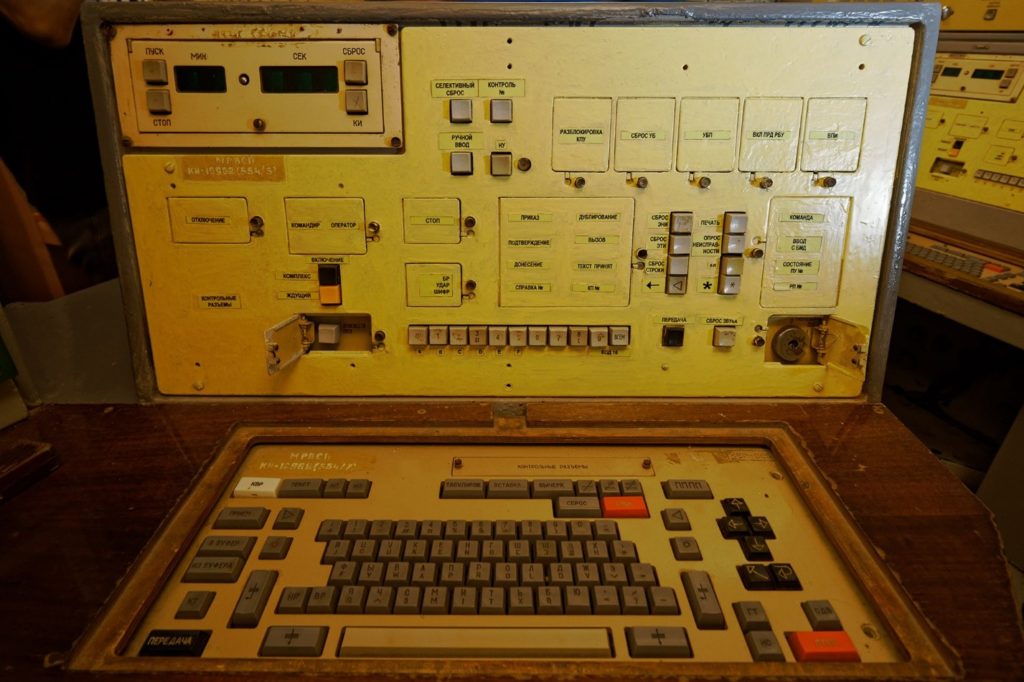

One of the reasons is that the tactical nuclear weapons from the times of the USSR is considered to be “battlefield nuclear weapons”. Although, in this case, the term “battlefield” is used for the strike range from several dozens of kilometers (nuclear warheads for large-calibre artillery) to several hundred of kilometers (Iskander or Kinzhal-type operational-tactical missiles and air bombs). Such “specialization” of the TNW means that after a decision to use it is made, the direct control of such weapons is carried out by not so high rank officers, who are situated not in the Kremlin, but directly at the front, in battlefield conditions. Correspondingly, the communication and control systems they use are much simpler and less protected than those which are used in the control systems of strategic nuclear weapons.

In this case, simplicity and weaker protection create the prerequisites for the TNW control system to be taken over by appropriately trained technicians that have access to analogical computing systems and communication means and know how the Russian TNW control systems functions. Exactly this situation will take place after the Russian tactical nuclear weapons is deployed in Belarus.
Which Belarusian enterprises and their specialists can participated in Lukashenka’s project aimed at seizing control of the Russian nuclear weapons
By the moment of the collapse of the Soviet Union, in the Belarusian Soviet Socialist Republic (BSSR) there were about 120 enterprises and organizations of the military-industrial complex of the USSR, including 15 scientific research institutes and design bureaus).
Belarusian military radio electronics, optics and optoelectronics were of particular significance. For instance, Gomel Design Bureau “Luch” and Gomel Radio Plant played a crucial part in the design and production of antennas for radar locators of missile attack warning systems, space surveillance systems, missile defense systems of the Soviet Union. Gomel Design Bureau “Luch” participated in creation of over-the-horizon radars 5N77, Duga 1 and 2, radar stations Daryal, Krona, Dunay, Volga, multipurpose radar station Don-2N, radar station Volna, radar station Atol of onboard radio reconnaissance system Coral of the command-and-control naval ship SSV-33 Ural, radar station 29Bb and others. At Gomel Radio Plant, antenna systems for Duga radar stations, antenna modules for Don-2NP and Don-2N radar stations were produced, as well as other appliances.
The leading organization creating automatic systems of troop control in group front line (district) through a battalion was situation in Minsk – Agat State Research and Production Association.
The Belarusian Optical & Mechanical Association (BelOMA) (Minsk) occupied the leading positions in the optical sphere of the USSR and specialized in extremely sophisticated optomechanical and optoelectronic equipment of military and space applications.
The Integral Research and Production Association (Minsk) was one of the leading Soviet manufactures of integrated circuits (first of all for the military-industrial complex and for the space industry), and the G.K. Ordzhonikidze Electronic Computing Machines Plant (now Minsk Computer Technology Production Association (MCTPA)) was one of the leading manufacturers of electronic computing machines used for both civilian and military purposes.
The Special Design and Technological Bureau of the Minsk Research Institute of Automation was the main developer of recognition systems in the Soviet Union.
As we can see, during the times of the USSR, almost everything used, among other things, in nuclear weapons control systems, was designed and manufactured in Belarus.
The modern Belarusian military-industrial complex continues to specilize in design and manufacturing of military radio electronics, optics and optoelectronics, software for military information systems and weapons control systems. Those are automated control systems of troops and weapons (Air Force and Air Aefense Forces ACS, ACS of Missile Forces, ACS of means of electronic warfare and means of reconnaissance), wired, fibre optic and radio communication systems for mobile and stationary ACS, aeronautical optoelectronic equipment and photogrammetric systems for acquisition of digital electronic land surface maps, navigational guidance support of high-precision weapons, fire command and control of armored force vehicles, modern opto-electronic sights for small arms, laser-beam infra-red searchlight for tanks and armored force vehicles, software application suites providing control of radio-locating, laser-optical and data systems of antiballistic missile defense, stations of warning of missile attacks, space surveillance systems, and others.
The leading Belarusian enterprises in those spheres are Open joint-stock company “AGAT – Control Systems” – Managing Company of Geoinformation Control Systems Holding (Minsk), JSC “AGAT-SYSTEM”, Agat – Electromechanical Plant JSC, Alevkurp JSC, JSC ‘Minsk Research Institute of Radio Materials’, OJS KB Radar – Managing Company of “Radar Systems” Holding, Peleng JSC, Republican Production Unitary Enterprise “Precise Electromechanics Plant”, BelOMO Holding, JSC “Sviazinvest”, Tetraedr UE (all of those are in Minsk), Zenit-BelOMO Joint Stock Company (Vileika, Minsk region), Molodechno Radio Plant SPUTNIK Republican unitary enterprise (Molodechno, Minsk region), JSC “Ekran” (Borisov, Minsk region), Gomel Design Bureau Luch OJSC (Gomel), OJSC “Display” (Vitebsk), Tekhnika Svyazi JSC (Baran, Vitebsk region), and others.
The work in the field of radio electronics, optics and optoelectronics is conducted both for the export (first of all, to the Russian Federation) and for the needs of own armed forces. Thus, OJS KB Radar has designed a family of Vostok 2D and 3D radar stations and the Rosa-RB air surveillance radar for detection of low-flying targets. In November, 2013, Vostok-D radar stations of meter range was adopted by radio-technical troops of the Air Force and Air Defence Forces of the Republic of Belarus, and in January, 2014, was put on combat duty as part of a division of the 49th Radio Engineering Brigade of the North-Western Operational Tactical Command of the Air Force and the Air Defence Forces. The Rosa-RB radar station was put into service in December, 2012. Design bureaus and plants of the Republic of Belarus have also designed and delivered to the armed forces automated control systems of air and air defense assets Bor, Poliana-RB, Rif-R, Rif-V.
First of all, for the development of Belarusian command systems of nuclear weapons in present days, the capacities of the OJSC “AGAT – Control Systems” can be used. It is the managing Company of Geoinformation Control Systems Holding. The structure of the holding includes five enterprises: OJSC “AGAT – Control Systems” (the managing company), Agat – Electromechanical Plant JSC, OJSC “NIIEVM”, Tekhnika Svyazi JSC and JSC “AGAT-SYSTEM”.
The holding traces its history back to 1969, when a specialized Research Institute of Automation (NIISA), its parent company, was created on the bases of Minsk Electromechanical Plant. Then, it functioned as Republican Unitary Research Enterprise “Research Institute of Automation Facilities”, the parent enterprise of the State Scientific and Production Association.
From 1986 to 2010, UE “NIISA” was the parent enterprise of the AGAT State Research and Production Association. In 2011, it was reorganized into the open joint-stock company “AGAT – Control Systems”, which later became the managing company of the holding “Geoinformation Control Systems”. The only shareholder of the open joint-stock company “AGAT – Control Systems”, as the managing company of the holding “Geoinformation Control Systems”, is the Republic of Belarus.
Business areas:
– automated control systems of military purpose;
– systems and means of communication;
– air and ground-based robotic platforms;
– automation in the energy sector;
– automation in the transportation sector;
– data protection.
Today, over 20 states are armed with modern models of products of OJSC “AGAT – Control Systems”. Among those models are:
BRDM-4B Intelligence complex,
R-186 Bogatyr-2 combined radio station,
R-414MBRP Sosna-2 radio relay station,
R‑432 Gorizont troposcatter station,
R-434 Citrus radio relay station,
P-240MB Caiman-KAS complex communications station.
When the nuclear weapons command systems were being designed, that enterprise was known as Republican Unitary Research Enterprise “Research Institute of Automation Facilities”, a scientific research establishment involved in comprehensive system research of the issues of global object management and practical implementation of such command systems.
UE “NIISA” was the parent organization of the AGAT State Research and Production Association, the leading enterprise of the defense industry sector first of the BSSR, and then of the Republic of Belarus, in the development and manufacturing of comprehensive integrated stationary and mobile automated control systems of troops, weapons, surveillance and electronic warfare, including means of communication, visual display units, computer aids in the protected execution, radar navigation equipment and army control and measuring instruments.
Over 50 years ago, a separate design bureau on the basis of Minsk Electromechanical Plant was reformatted into a Research Institute of Automation Facilities (NIISA). The enterprise had a task, very important for the defence of the Sovite Union, to build automated control systems over armed forces for the levels of frontline (military district) – army (corps) – division (brigade) – regiment- battalion (division, battery, squadron). Also, the task to develop a comprehensive integrated automated control systems for all branches and types of troops in the indicated levels.
In 1970–1980, NIISA developed a number of systems and complexes based on the latest computing, communication and data transfer means of thattime. Such automated battlefield control systems as Maneuver and the ones that made part of it, like Etalon, Polyana-D4M, Iva and Pori-P2 passed all the kinds of tests and were adopted for service. The Manevr ACS over troops and weapons and its component the Etalon, Polyana-D4M, Iva, Ranzhir, Pori-P2 ACS and others passed all tests and were introduced into service. Consequently, with direct participation of NIISA specialists, several generations of means and systems of control were created.
In 1986, the State Research and Production Association AGAT was formed on the basis of NIISA and some of the USSR enterprises. By the beginning of the 1990s, the number of employees of the association exceeded 35,000 persons.
When, already in the Republic of Belarus, the State Authority for Military Industry made a decision to establish a specialized holding, involved in development and manufacture of systems of control and navigation, a corresponding order of the president was issued. Thus, by the end of 2011, there appeared the open joint-stock company “AGAT – Control Systems”, which later became the managing company of the holding “Geoinformation Control Systems”.
SKB Kamerton JSC was included in the holding as its subsidiary in July of the 2013. Created in Soviet times on the basis of one of the subdivisions of AGAT enterprise, it is currently a network operator of the Republic of Belarus in the sphere of navigation activity. Its specialists create a unified navigation and time system of the Republic of Belarus.
The second enterprise which was involved, among other things, into manufacturing of nuclear-weapon command system in Soviet times (in particular, on submarines, but not only), is once famous in Minsk, Minsk Instrument-Making Plant named after V.I. Lenin. Later it became JSC “Minsk Instrument-Making Plant”, which was then included into JSC “AMKODOR”– holding managing company” and changed its name into Amkodor-Belvar OJSC. The transformation of the enterprises began after Lukashenka had signed the decree 274 “”On some measures for the «Amkodor» development” dated June 27, 2011, according to which the Company undertook to incorporate three enterprises before December 31, 2011, JSC “Minsk Instrument-Making Plant” among them.
The story of the JSC “Minsk Instrument-Making Plant” began in 1939, when construction of the first radio enterprise in Belarus, Minsk Radio Plant, started on the basis of the plant “Derevoobdelochnik”. On November 6, 1940, a meeting took place devoted to the issue of first radio products: radio sets KIM and PIONEER. That date is considered to be the birthday of Minsk Radio Plant. After the war, in February, 1946, the enterprise was rebuilt and began manufacturing its main goods, radio sets, and in 1950 – radio measuring devices. In 1958, Minsk Radio Plant was transformed into Minsk Instrument-Making Plant named after V.I. Lenin, and in 1971 MPO named after V.I. Lenin was created on its basis.
Till the year 1991, the association made part of the Military-Industrial Complex of the USSR and was involved into manufacturing of radiation-measuring, metrological products and of special purpose equipment. After the collapse of the Soviet Union, it was subject to major conversion. In 1992, the MPO named after V.I. Lenin was reorganized into Belarusian Production Association of Radio Electronics “BelVAR”. In 1996 it was reorganized in the State Enterprise “BelVAR”. In 1997, in the result of conversion into joint-stock company, JSC “Minsk Instrument-Making Plant” was created. In October, 2011, the joint stock company “Minsk Instrument-Making Plant” was incorporated into JSC “AMKODOR” and changed its name into Amkodor-Belvar OJSC.
Currently, Amkodor-Belvar OJSC. is manufacturing household electronics, radio measuring medical and radiation-survey instruments, accumulator starting batteries and special equipment products. Having preserved the range of products and the personnel, in accordance with the applied development strategy of the JSC AMKODOR, the administration of the company is planning to implement manufacture of different assembly units and electric devices for Amkodor make machines.
The third enterprise from our list is Integral. It is a Belarusian manufacture of integrated circuits and liquid crystal indicators founded in 1962 and situated in Minsk. Together with Zelenograd enterprises «Micron” and “Angstrem-T” (growing up from under the wing of the NGO “Research center”), it was a major manufacturer of integrated circuits in the USSR. It kept conducting its activity also after the collapse of the Soviet Union, having managed to keep and maintain its production base and its personnel.
The structure of Integral includes such specialized enterprises as:
– Belmikrosistemy NTC,
– UE Semiconductor Devices Factory,
– UE Transistor Plant
– UE Tsvetotron Plant (Brest),
– SKB NEMIGA RUE,
– Electronika Plant RUE,
– SKB Zapad RUNIP,
– UE Kamerton Plant,
– Elektromodul OJSC,
– Integraltehnis DRUP,
– Integral-KART PE,
– Vitebsk Design Bureau of Automated Control Systems PKB ACS RUP,
– UE Statinfotech.
In Soviet times, the main part of the products of Integral was designed for the needs of the defence. The arms race launched by the USSR and the USA in the 80s was the reason Integral prospered. Before Perestroika, the association produced over 60-70% of the spare parts for Soviet computers and control systems. In particular, they included dynamic memory microcircuits of 65 and 256 kilobit and multiple logic families, as well as semiconductor devices. In those times, Belmikrosistemy NTC designed, and the plants mastered over 100 of new products each year. Until now, the microcircuits of Integral are implemented in Russian weapon systems, fly on board of the MIR Station, and so on.
Summary
Of course, we cannot definitely state, whether Aliaksandr Lukashenka is planning to seize control over Russian nuclear weapons after it is deployed in Belarus or not, however, we hear his statements and see a lot of prerequisites for that:
– multiple public complaints of Lukashenka that in the 90s Belarus voluntarily renounced nuclear weapons and completed their removal from its territory,
– the statements that Belarus is also going to control Russian tactical nuclear weapons deployed in Belarus,
– a potential technical and military capability of Minsk to seize control over tactical nuclear weapons from Moscow.
We need a campaign in Belarus to counter the deployment of tactical nuclear weapons in the country and for the disarmament of Lukashenka.








